|
Brief introduction
Embracing Innovation for Digital Transformation 
- Explore the importance of embracing innovation as a catalyst for digital transformation in MSMEs
- Learn about the mindset and strategies needed to foster a culture of innovation, adapt to disruptive technologies, and drive organisational change management towards digital resilience
Harnessing the Power of Innovative Digital Solutions 
- Discover the potential of digital solutions such as cloud computing, (data) analytics, Automation and AI for MSMEs
- Gain insights into how these technologies can optimise business processes, enhance decision–making, and create competitive advantages in the digital landscape
Implementing Innovative Digital Solutions for Business Growth 
- Learn how to effectively implement and leverage innovative digital solutions within MSMEs
- Explore practical approaches to adopting and integrating technologies such as cloud computing, analytics, and AI into business operations
- Understand the challenges and best practices associated with successful implementation and utilisation of these technologies for sustainable business growth
Innovation for Digital Transformation
Introduction to Digital Transformation in MSMEs 
Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital solutions into all aspects of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value to customers.
MSMEs are called to adopt and integrate digital technologies to stay competitive and reach a long-term success.
In this content, the digital transformation is a key driver for MSMEs to enhance:
- Efficiency: Streamlining processes to accomplish tasks with minimal resources, time and waste, ensuring optimal productivity
- Agility: Adapting and responding to changes in the business environment
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Elevating customer services and satisfaction through personalised interactions
From traditional state to digital transformation: the Transformation Process Diagram

The process reflects and consists of 4 phases:
- The state before digital transformation
- The adoption of digital technologies
- The integration of digital technologies into various aspects and operations
- The achieved state of digital transformation
Building a Culture of Innovation 

In the realm of innovative digital solutions and as an initial step in the digital transformation journey – transitioning from a traditional state to digital adoption – MSMEs need to shift in mindset towards innovation.
Tips for MSMEs for internally building a culture of innovation:
- From “This is how we have always done it” to “How can we do it better?”
- Open communication and idea-sharing – brainstorming sessions and cross-functional teams working on innovation
- Intrapreneurship – a monthly ‘Innovation Day’ where employees dedicated time to work on personal projects, leading to the development of a successful new product and / or innovative processes
Adapting to Disruptive Technologies 
From identification to adoption of disruptive technologies: visual representation via a flowchart
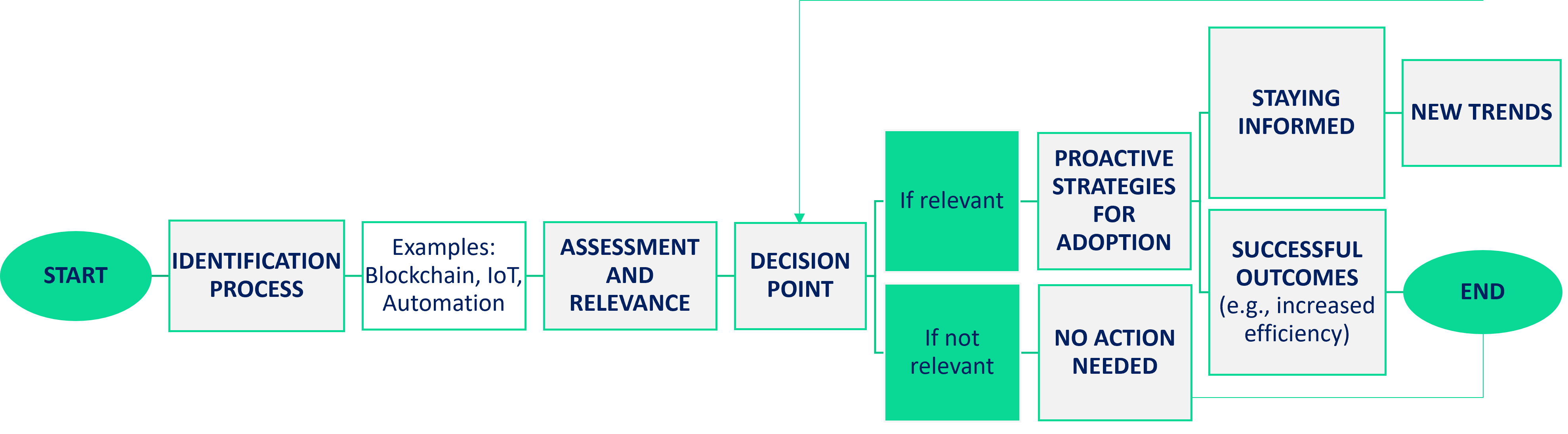
Change Management for Digital Resilience 
In the adoption of innovation and digital technologies for digital transformation, an operational and concrete push can come from change management. As MSMEs embrace disruptive tech, pivotal factor is effective change management.
Change management emerges as the strategic approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organisations from their current state to desired future state. It involves careful planning, communication and strategies and it propels operational shifts within organisations, by minimising resistance and driving organisational change.
Aiming to digital resilience as an outcome for sustained growth and adaptability, here are some strategies for effective change management with related concrete example:
- Clear Communication Plans: Regular news for sharing progress updates within organisation
- Employee Involvement: Cross-functional teams and ‘take the lead’ days for alternative and innovative collaboration on the implementation of innovative digital solutions
- Training Programmes: Courses and workshops to enhance skills, knowledge and proficiency
Harnessing the Power of Innovative Digital Solutions
Overview of Innovative Digital Solutions 
In realising the potential for competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving digital landscape, here is an overview of key innovative digital solutions designed to empower MSMEs:
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Cloud Computing
|
(Data) Analytics
|
Automation |
Artificial Intelligence
|
|
Explore the flexibility and scalability of cloud-bases solutions
|
Harness the power of data for informed decision-making
|
Enhance efficiency through the automated execution of tasks
|
Unlock the potential of AI for business optimisation
|
Let’s in-depth explore each digital solution in the following sections – discover how these technologies can streamline operations and enhance efficiency within MSMEs.
Cloud Computing for MSMEs 
|
Cloud Computing is a paradigm that concerns the delivery of computer services over the internet. It includes services such as storages, processing, networking.
In these terms, MSMEs can access and utilise computing resources without the need for on-site infrastructure, offering a flexible and scalable solution.
|
 |
BENEFITS
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on business needs
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the resources used, reducing upfront costs
- Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection
USE CASES FOR MSMEs
- Data Storage and Backup: Securely store and backup critical business data
- Collaboration: Facilitate teamwork with cloud-based collaboration tools
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Leverage cloud-hosted software applications
Data Analytics and Informed Decision-Making 
|
Data Analytics involves the examination of raw data through sophisticated tools to uncover insights, trends and patterns that inform strategic decision-making.
|
 |
KEY COMPONENTS
- Descriptive Analytics: Understand what has happened through historical data analysis
- Predictive Analytics: Forecast future trends and outcomes based on patterns
- Prescriptive Analytics: Recommend actions for optimal outcomes
BENEFITS
- Informed Decision-Making: Make data-driven decisions based on actionable insights
- Operational Efficiency: Streamline processes and identify areas for improvement
- Competitive Advantage: Gain a competitive edge by leveraging data for innovation
USE CASES FOR MSMEs
- Customer Insights: Understand customer behaviour and preferences for targeted relationship
- Supply Chain Optimisation: Enhance efficiency and reduce costs in the supply chain
- Financial Forecasting: Improve budgeting and financial planning
Automation for Tasks Efficiency 
|
Automation involves leveraging technology and digital solutions to execute tasks with minimal human intervention, optimising processes and freeing up valuable time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives.
|
 |
BENEFITS
- Efficiency Gains: Streamline repetitive tasks, reducing manual effort and potential errors
- Resource Optimisation: Allocate human resources to more complex and strategic functions
- Consistency: Ensure consistent and standardized task execution
KEY AREAS IN MSMES
- Data Entry and Processing: Automate routine data entry tasks, minimizing errors and saving time
- Customer Support: Implement chatbots and automated responses to handle common customer queries
- Workflow Automation: Streamline internal processes like approvals and document routing
AI for Business Optimisation 
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a horizontal solution to all others that involves the application of advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to empower businesses with insights, automation, and strategic decision-making.
|
 |
BENEFITS
- Data-driven Insights: Distil insights from vast datasets for informed decision-making capabilities
- Process Automation: Witness the seamless optimisation of complex processes through intelligent automation
- Predictive Capabilities: Foresee trends and outcomes based on historical data, thereby enabling proactive and future-oriented strategies
KEY APPLICATIONS IN MSMEs
- Predictive Analytics: Forecast future trends, enabling organisations to proactively refine business strategies
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Integrate AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to enhance customer interactions, streamline support, and elevate overall user experiences
- Personalised Marketing: Tailor and support the realisation of marketing strategies with precision, catering to individual customer preferences and behaviours
Innovative Digital Solutions for Business Growth
Effective Implementation Strategies 
This section is a compass for steering your business towards growth through the effective implementation of innovative digital solutions. Successful implementation is not just about adopting technologies but orchestrating a strategic approach that ensures seamless integration and tangible business outcomes. This approach involves:
- Define Clear Objectives (DCO in the next slide): Establish specific, measurable, and achievable goals for each digital solution to align with overall business objectives
- Prioritise Solutions (PS in the next slide): Sequence the implementation based on priority, focusing on solutions that deliver immediate impact or address critical needs
- Cross-functional Collaboration (CC in the next slide): Foster collaboration among different departments to ensure a holistic and integrated implementation approach
Consequently, implementation is accompanied by continuous monitoring and optimisation, as follows:
- Performance Metrics: Establish KPIs to measure the success and impact of digital solutions on business objectives
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback loops to gather insights from users and stakeholders, allowing for continuous improvement
- Scalability: Plan for the scalability of digital solutions as business needs evolve, ensuring long-term relevance and growth
Practical examples of implementation strategies for our innovative digital solutions (see unit 2 for reference):
|
Cloud Computing
|
(Data) Analytics
|
Automation |
Artificial Intelligence
|
|
DCC: Establish objectives like migrating data to the cloud, reducing on-premise infrastructure, and improving remote access to enhance overall business agility
|
DCC: Set objectives such as leveraging data analytics to enhance decision-making, optimize processes, and gain a competitive advantage
|
DCC: Clearly state the objectives of automation, whether to increase operational efficiency, reduce errors, or free up human resources for strategic tasks
|
DCC: Outline objectives such as using AI for predictive analytics, implementing chatbots for customer interactions, and personalizing marketing efforts
|
|
PS: Start with non-critical applications, ensuring a smooth transition before moving essential systems to the cloud
|
PS: Initiate with descriptive analytics to understand historical data before advancing to predictive and prescriptive analytics
|
PS: Begin with automating repetitive tasks like data entry before progressing to more complex processes like workflow automation
|
PS: Start with a focused AI application, like implementing a chatbot for customer support, before expanding to more complex AI solutions
|
|
CC: Engage IT, finance, and operations teams to align cloud adoption with organisational goals and financial considerations
|
CC: Collaborate with marketing, operations, and IT teams to ensure data analytics aligns with specific departmental needs
|
CC: Engage HR, operations, and IT teams to identify areas for automation and ensure alignment with overall business goals
|
CC: Collaborate with IT, marketing, and customer support teams to integrate AI seamlessly and address the needs of each department
|
Challenges and Best Practices for Integration in Business Operations 
Embarking in effective integration in operations for business growth comes with its set of challenges. Here are some challenges in implementing innovative digital solutions – with related best practices to overcome them:
|
Resistance to Change: Overcoming reluctance among employees to embrace new technologies and workflows
|
Integration Complexity: Managing the integration of multiple digital solutions without disrupting existing operations
|
Data Security Concerns: Addressing apprehensions related to the security and privacy of data
|
Skill Gaps: Bridging the gap in skills required for effectively using and maintaining digital solutions
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Change-Ready Culture: Communicate the benefits to instil enthusiasm and reduce resistance
|
Comprehensive Integration Strategy: Conduct an assessment of existing systems to streamline the process
|
Data Security: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations and standards and implement cybersecurity measures
|
Continuous Learning: Provide ongoing training to empower staff with new skills and knowledge
|
Practical examples for the integration of innovative digital solutions (see unit 2 for reference) into business operations:
| Cloud Computing |
(Data) Analytics |
- Data Migration Complexity: Transitioning large volumes of data to the cloud without disrupting ongoing operations
- Cost Management: Controlling and optimising cloud-related costs as usage scales
- Security Concerns: Addressing apprehensions about data security and compliance in a cloud environment
- Vendor Lock-in: Mitigating the risk of dependence on a single cloud service provider
|
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data for meaningful analysis
- Skill Gaps: Bridging the gap in data analytics skills among employees.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating diverse data sources for a holistic analysis
- Managing Big Data: Effectively handling and analysing large volumes of data
|
 |
 |
- Pilot Migration: Start with a small-scale data migration to identify and address challenges before a full-scale transition
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Utilize tools to monitor and optimize cloud resource usage, ensuring cost-effectiveness
- Encryption and Compliance: Implement robust encryption protocols and adhere to industry-specific compliance standards
- Multi-Cloud Strategy: Consider a multi-cloud approach to avoid dependency on a single vendor and enhance flexibility
|
- Data Governance Framework: Establish a data governance framework to maintain data quality standards
- Training Programmes: Invest in training programs to enhance the data analytics skills of employees
- Data Integration Platforms: Utilize robust data integration platforms to streamline the integration of diverse data sources
- Scalable Infrastructure: Implement scalable infrastructure to manage and process big data effectively
|
| Automation |
Artificial Intelligence |
- Identifying Automation Opportunities: Recognizing which tasks and processes can benefit from automation
- Employee Resistance: Overcoming resistance to the adoption of automated workflows
- Ensuring Reliability: Building trust in the reliability and accuracy of automated processes
- Costs of Implementation: Managing initial costs associated with implementing automation
|
- Ethical Concerns: Navigating ethical considerations related to AI applications
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AI seamlessly with existing systems and workflows
- Explainability: Ensuring transparency and explainability in AI-driven decision-making
- Data Bias: Mitigating bias in AI algorithms and ensuring fair and unbiased outcomes
|
 |
 |
- Automation Audits: Conduct audits to identify and prioritize tasks suitable for automation
- Change Management Programmes: Implement change management programs to address employee concerns and foster a positive attitude toward automation
- Quality Assurance Measures: Implement rigorous quality assurance measures to ensure the reliability of automated processes
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to justify and optimize the costs of automation
|
- Ethics Guidelines: Develop and adhere to ethical guidelines governing AI applications within the organization
- Collaboration with IT: Collaborate closely with IT teams to ensure smooth integration of AI into existing systems
- Explainable AI Models: Prefer AI models that offer transparency and can provide explanations for their decisions
- Diverse and Representative Data: Ensure diversity and representation in the training data to minimize bias in AI algorithms
|
Summing up 
|
 Digital Transformation as Strategic Imperative: Digital Transformation as Strategic Imperative:
- Digital transformation is not a choice but a strategic imperative for MSMEs aiming for sustained growth
- Embracing innovation is crucial for cultivating resilience, agility, and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving business landscape
|
 |
 Strategic Implementation Drives Success: Strategic Implementation Drives Success:
- Success in adopting cloud computing, data analytics, automation, and AI hinges on a strategic and well-planned implementation
- Clear objectives, thoughtful integration, and cross-functional collaboration are paramount
|
|
 Navigation of Challenges with Best Practices: Navigation of Challenges with Best Practices:
- Challenges are inherent in digital transformation journey, but proactive identification and application of best practices pave the way for success
- Establishing a change-ready culture, robust data security measures, and ongoing skill development are key to overcoming hurdles
|
 Cultivating Continuous Learning and Adaptability: Cultivating Continuous Learning and Adaptability:
- In the dynamic digital landscape, continuous learning is essential for organisational and individual growth
- Adaptability ensures that MSMEs are not only prepared for current challenges but are also future-ready to embrace emerging technologies
|
|

